1. Chiropractic Care
Key peptides: BPC-157, TB-500
Healing is just as important as alignment in managing tissue injuries, postural strain, and joint dysfunction.
BPC-157, a synthetic peptide derived from a gastric protein, has been shown to accelerate tendon and ligament repair, promote angiogenesis, and protect against soft tissue damage under mechanical stress.
TB-500, a synthetic fragment of Thymosin Beta-4, is also being examined for its potential to promote cellular regeneration, particularly in muscle and connective tissues.
A study by Malinda et al. reported that administration of TB-500 in rats led to a 42% improvement in wound healing status compared to the control group by day four.
The therapeutic targets of these peptides align closely with the functional goals of musculoskeletal care.
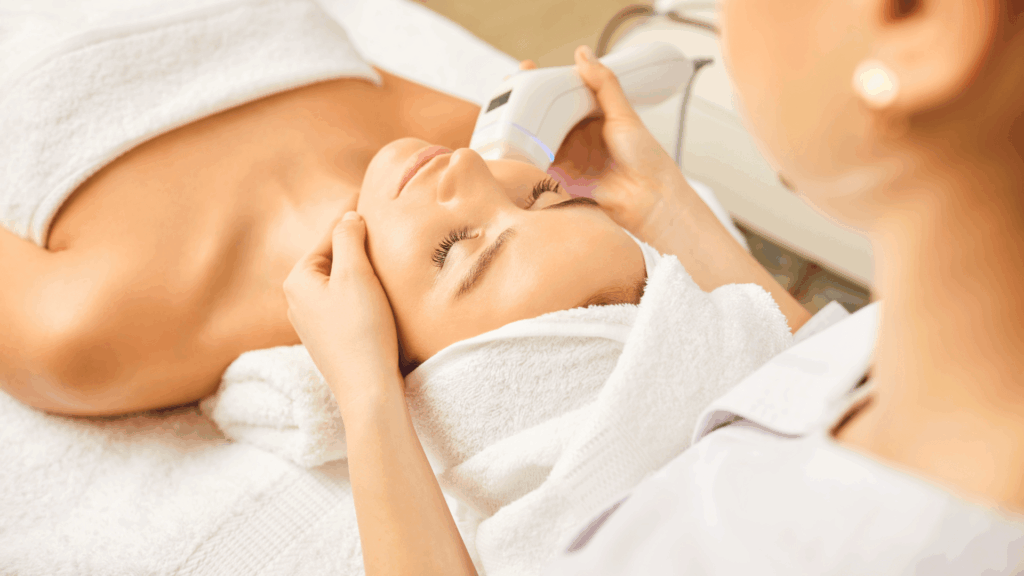

2. Aesthetic Medicine
Key peptides: CJC-1295, Ipamorelin, GHK-Cu
Clinics offering non-surgical rejuvenation are beginning to seek peptides that work internally to enhance visible, external outcomes.
CJC-1295, a GHRH analog, and Ipamorelin, a selective growth hormone secretagogue, have both demonstrated the ability to increase growth hormone and IGF-1 levels in humans.
These increases are associated with improved collagen production, skin thickness, and overall tissue repair.
GHK-Cu, a naturally occurring tri-copper-binding peptide, meaning that it is made up of three amino acids, is one of the most researched peptides in aesthetic medicine.
First identified in the 1970s, it has been the subject of over 100 scientific publications exploring its role in collagen production, angiogenesis, and tissue repair.
Studies show it supports wound healing, reduces inflammation, and improves skin elasticity, making it a staple in skin-focused protocols and regenerative therapies.
3. Sports & Orthopaedic Medicine
Key peptides: BPC-157, TB-500, IGF-1 LR3
Athletes and high-performance patients often require accelerated recovery from injury or overuse.
BPC-157, short for “Body Protective Compound-157,” is a synthetic peptide derived from a naturally occurring protein found in the stomach.
Preclinical studies have shown it accelerates healing in tendons, ligaments, and even bone.
It also appears to support joint mobility and tissue repair following injury, which is why it’s frequently referenced in musculoskeletal and sports medicine research.
TB-500 is a synthetic version of a segment of thymosin beta-4, a protein involved in tissue regeneration.
It’s being studied for its ability to influence actin regulation and promote cellular migration, two key mechanisms involved in soft tissue recovery.
Its potential to improve flexibility and reduce inflammation has made it of interest in performance-focused protocols.
These peptides are of particular relevance in sports medicine clinics aiming to reduce downtime and support high-functioning tissue recovery, without relying solely on anti-inflammatory or corticosteroid medications.

4. Hormone Optimization & Vitality Clinics
Key peptides: Thymosin Alpha-1 (TA-1), CJC-1295, NAD+
Clinics focused on longevity, immune balance, and hormonal support have long recognized the benefits of integrating peptides that target systemic resilience.
Thymosin Alpha-1 (TA-1) has been used in more than 30 countries and studied in over 30 clinical trials. It plays a documented role in T-cell activation and immune modulation, particularly in cases of immune suppression, chronic infection, or inflammation.
CJC-1295, best known for its ability to increase endogenous GH and IGF-1 levels, is already mentioned in the context of skin and recovery.
Still, it also plays a central role in hormone optimization protocols aimed at improving lean body mass, sleep quality, and energy regulation, all key concerns in longevity-focused care.
NAD+, a critical coenzyme in cellular energy production and DNA repair, has emerged as a foundational molecule in age-management research.
Studies suggest that restoring NAD+ levels may help improve mitochondrial efficiency, reduce oxidative stress, and slow cellular aging making it a focal point in protocols designed to enhance vitality and metabolic health over time.
Peptide therapy continues to grow, not just in popularity, but in clinical depth.
What stands out is not merely the volume of peptides available, but the breadth of physiological systems they’re being explored for.
Want Deeper Insights into How Peptides Intersect with Metabolic Health?
Join our newsletter for early insights into emerging blends, research developments, and strategies shaping the future of peptide therapy.